China's CNC (Computer Numerical Control) factories have become integral to global manufacturing, delivering high-precision components across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. This article provides a comprehensive examination of the technology, precision, and quality standards that define China's CNC manufacturing sector. By focusing on technical details, operational processes, and industry practices, we aim to offer a systematic and authoritative overview without speculative trends or challenges.
Overview of CNC Technology in China
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled tools to remove material from a workpiece, creating precise parts based on digital designs. In China, CNC factories leverage advanced machinery and software to produce components with tight tolerances and consistent quality. The integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software ensures accurate translation of designs into machine instructions, typically using G-code and M-code.
China's CNC industry has grown significantly, driven by robust industrial capacity and government initiatives like the "Made in China 2025" strategy, which emphasizes high-end manufacturing. Factories are equipped with a range of CNC machines, including milling machines, lathes, routers, and laser cutters, each tailored to specific materials and applications. The adoption of multi-axis systems, such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machines, enhances the ability to produce complex geometries in a single setup, improving efficiency and precision.
Key manufacturers, such as General Technology Group Dalian Machine Tool Corporation and SINO CNC Machinery, produce a variety of CNC equipment, from vertical machining centers to high-precision lathes. These machines are designed for durability, with components like high-strength meehanite castings and advanced servo motors ensuring stability during high-speed operations.
Precision in CNC Machining
Precision is a cornerstone of China's CNC factories, enabling the production of components with tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm for high-end applications. Precision is achieved through a combination of advanced machinery, meticulous programming, and rigorous quality control.
Machine Capabilities: Modern CNC machines in China feature multiple axes of movement, with 5-axis systems being particularly prevalent in aerospace and medical manufacturing. These machines can access five out of six sides of a workpiece in a single operation, reducing repositioning errors. For example, a 5-axis CNC mill uses linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotational axes (A, B), allowing complex cuts at precise angles. High-precision ball screws and linear encoders minimize backlash, ensuring consistent accuracy during repetitive tasks.
Programming and Control Systems: CNC systems rely on sophisticated control units, such as those developed by Fanuc and Mitsubishi, or domestic alternatives like First Automation’s CNC units. These systems translate CAD/CAM designs into motion control signals with nanometer-level interpolation. For instance, First Automation’s metal-cutting CNC system achieves precision measured in nanometers, suitable for aerospace components where minute deviations can impact performance.
Material Versatility: Chinese CNC factories process a wide range of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, plastics, and composites. Each material requires specific tools and parameters. For example, machining titanium demands low cutting speeds (50-100 m/min) and high-pressure coolant to manage heat, while aluminum allows higher speeds (300-600 m/min) for faster production.
| Материал | Typical Cutting Speed (m/min) | Coolant Requirement | Тип инструмента |
|---|---|---|---|
| Алюминий | 300-600 | Умеренный | Carbide End Mills |
| Нержавеющая сталь | 100-200 | Высокий | High-Speed Steel Drills |
| Титан | 50-100 | High-Pressure | Coated Carbide Tools |
| Пластмассы | 200-400 | Низкий | Polycrystalline Diamond Tools |
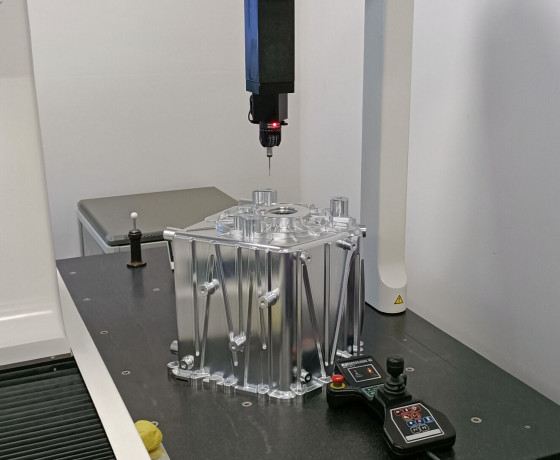

Quality Control Standards
Quality assurance in China's CNC factories is systematic, involving multiple stages of inspection and testing to ensure components meet stringent specifications. Factories adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications for automotive (IATF 16949) and medical (ISO 13485) applications.
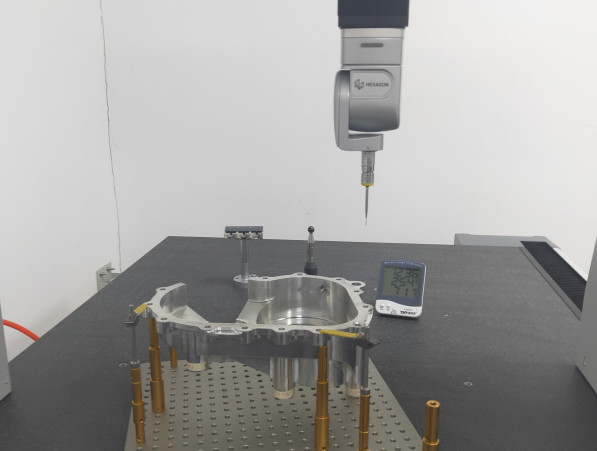
Inspection Processes: Precision components undergo dimensional inspections using coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and laser scanners, which verify tolerances to within microns. Surface finish is evaluated using profilometers, ensuring smoothness for applications like medical implants (Ra 0.2-0.8 µm). Non-destructive testing (NDT), such as ultrasonic and X-ray inspections, detects internal defects in critical parts.
Real-Time Monitoring: Many CNC machines are equipped with real-time feedback systems, including temperature sensors and displacement sensors, to monitor thermal errors and positional accuracy. For example, a vertical high-speed CNC machine may use seven temperature sensors and two displacement sensors to maintain precision during extended operations.
Documentation and Traceability: Factories maintain detailed records of machining parameters, material batches, and inspection results. This traceability ensures accountability and facilitates root-cause analysis if issues arise. For instance, PCBWay, a prominent CNC service provider, emphasizes contractual obligations to safeguard client data and ensure consistent quality across orders.
Key CNC Machine Types and Applications
China's CNC factories deploy a variety of machine types, each optimized for specific tasks and industries. The following outlines the primary CNC machines and their applications, highlighting their technical specifications.
CNC Milling Machines: These machines use rotary cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. Vertical machining centers (VMCs), such as those from SINO CNC Machinery, feature spindle speeds up to 12,000 RPM and tool capacities of 24-40 tools. They are ideal for producing flat surfaces, slots, and complex contours in automotive and electronics components.
CNC Lathes: CNC lathes rotate the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, suitable for cylindrical parts like shafts and bushings. High-precision lathes, such as those from Hardinge, achieve tolerances of ±0.002 mm and are used in aerospace for turbine components. Turn-milling composite machines combine turning and milling, reducing setup times by completing multiple processes in one clamping.
Laser Cutting Machines: Fiber laser cutters, introduced by manufacturers like STYLECNC, offer cutting speeds up to 30 m/min for sheet metal. They use 1064nm fiber lasers for metals and CO2 lasers for non-metals, with precision down to ±0.05 mm. These machines are widely used in automotive and consumer electronics for intricate designs.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): EDM machines shape hard materials like titanium through electrical sparks, achieving surface finishes as fine as Ra 0.1 µm. They are critical for mold-making and aerospace components requiring intricate geometries.
| Тип машины | Key Specifications | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Фрезерование с ЧПУ | Spindle Speed: 8,000-12,000 RPM, Tool Capacity: 24-40 | Automotive, Electronics |
| Токарный станок с ЧПУ | Tolerance: ±0.002 mm, Max Diameter: 500 mm | Aerospace, Medical |
| Лазерная резка | Cutting Speed: 30 m/min, Precision: ±0.05 mm | Sheet Metal, Consumer Electronics |
| EDM | Surface Finish: Ra 0.1 µm, Max Current: 50 A | Mold-Making, Aerospace |
Operational Efficiency and Factory Practices
China's CNC factories prioritize operational efficiency through streamlined workflows and advanced automation. Factories integrate automated tool changers (ATCs) and robotic arms to minimize downtime and enhance productivity. For example, a CNC machine with an ATC can switch tools in under 5 seconds, significantly reducing cycle times for multi-tool operations.
Factory Layout and Maintenance: Factories are designed with optimized layouts to facilitate material flow and machine accessibility. High-strength cast iron machine bodies, as used by Yangsen, ensure stability and vibration resistance, critical for maintaining precision during high-speed machining. Regular maintenance, including cleaning with specialized agents and checking geometric accuracy (e.g., level readings not exceeding 0.02/1000 mm for high-precision machines), extends equipment lifespan.
Skilled Workforce: Operators and programmers undergo rigorous training to master CNC systems and CAD/CAM software. Companies like Universal Technical Institute (UTI) offer programs in China, teaching skills from blueprint reading to machine setup. This expertise ensures that complex parts are produced with minimal errors, even for small-batch or custom orders.
Customization and Scalability: Chinese CNC factories excel in providing tailored solutions, from prototyping to high-volume production. For instance, PCBWay offers rapid prototyping with lead times as short as one day, catering to industries requiring quick turnaround for new product launches.

Kesu CNC: Crafting Every Detail to Global Excellence
From ultra-tight tolerances of ±0.001mm to precise machining across diverse materials, Kesu embodies the core strength of China's CNC manufacturing. Leveraging 5-axis collaboration technology to conquer complex geometries, real-time monitoring systems to lock in micron-level precision, and fortified by ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications, we set uncompromising quality standards. Whether it’s titanium alloy components for aerospace or mirror-finish medical implants, Kesu delivers with automated efficiency and tailored solutions, making every product a testament to precision and reliability—partnering with global manufacturing to forge a high-precision future.
Заключение
China's CNC factories represent a pinnacle of precision manufacturing, combining advanced technology, stringent quality control, and efficient operations to meet global demands. By leveraging multi-axis machines, sophisticated control systems, and comprehensive quality assurance, these factories produce high-precision components for critical industries. The systematic approach to machining, from design to inspection, underscores their reliability and technical expertise. As a key player in the global manufacturing landscape, China's CNC sector continues to deliver consistent, high-quality results through well-established processes and robust infrastructure.
