An automatic transmission is a sophisticated system that enables seamless gear shifting in vehicles without driver intervention. It relies on a combination of hydraulic, mechanical, and electronic components to transfer power from the engine to the wheels efficiently. This article provides a detailed overview of the primary parts of an automatic transmission, their functions, technical parameters, and manufacturing processes.
What Is Automatic Transmission?
An automatic transmission manages gear ratios through a combination of fluid dynamics, gear sets, and electronic controls, ensuring optimal engine performance across various driving conditions. Key components include the torque converter, planetary gear set, hydraulic system, clutch packs, bands, oil pump, valve body, and transmission control module (TCM). Below, we detail each component’s role, specifications, and manufacturing processes, emphasizing precision and technical accuracy.
Key Components of an Automatic Transmission
The following sections outline the primary parts, their functions, parameters, and manufacturing methods. Tables are used to present technical specifications and manufacturing details clearly.
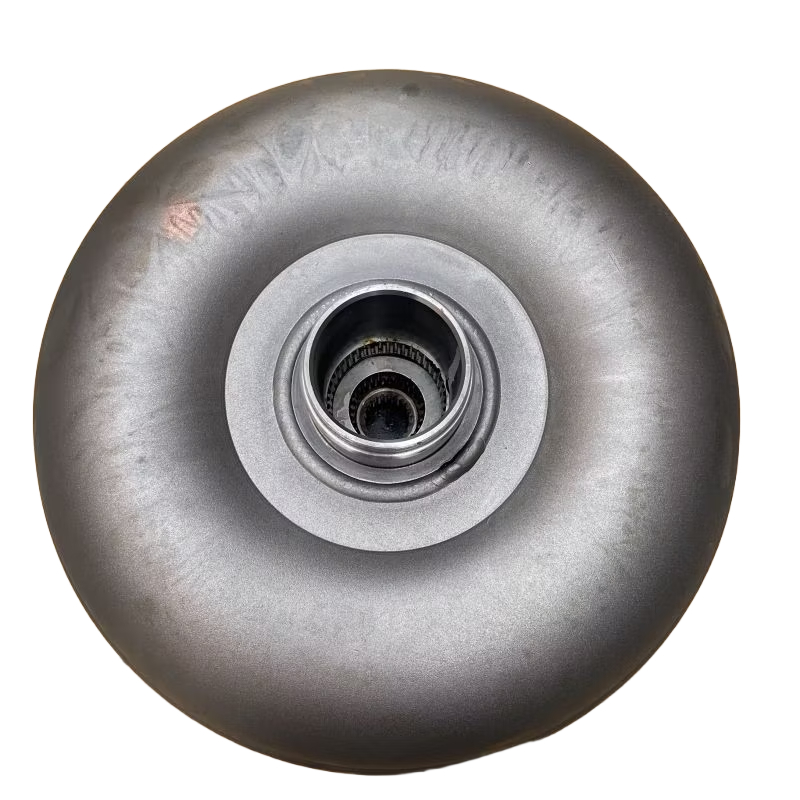

1. Torque Converter
The torque converter is a fluid coupling device that transfers power from the engine to the transmission, enabling idling without stalling and providing torque multiplication.
- Funktion: Transfers engine power to the transmission input shaft, facilitates smooth gear transitions, and multiplies torque at low speeds.
- Components:
- Impeller: Accelerates transmission fluid, connected to the engine crankshaft.
- Turbine: Receives fluid energy, connected to the transmission input shaft.
- Stator: Redirects fluid to enhance torque multiplication, equipped with a one-way clutch.
- Lock-up Clutch: Engages at higher speeds for direct mechanical connection, improving efficiency.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durchmesser | Varies by vehicle type | 200–350 mm | Stamping and welding (sheet metal for housing) |
| Fluid Capacity | Transmission fluid volume | 8–12 liters (including transmission) | N/A (fluid not manufactured) |
| Stall Speed | Engine RPM at full throttle, no movement | 2000–3500 RPM | Precision machining for impeller/turbine blades |
| Torque Multiplication | Ratio of output to input torque | 1.5:1 to 2.5:1 | Assembly of stamped and machined parts |
| Material | Housing and internals | Steel, aluminum | Casting (stator), forging (clutch components) |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Impeller and Turbine: Formed by stamping sheet metal into precise shapes, followed by welding to create sealed chambers. Blades are machined to ensure optimal fluid flow.
- Stator: Cast from aluminum or steel, with blades machined for precise angles to maximize torque multiplication.
- Lock-up Clutch: Friction plates are manufactured using composite materials bonded to steel cores, with precision assembly to ensure reliable engagement.
- Assembly: Components are welded and balanced to minimize vibration, with rigorous quality checks for fluid-tight seals.
- Maintenance: Requires fluid changes every 30,000–60,000 miles to prevent contamination.
2. Planetary Gear Set
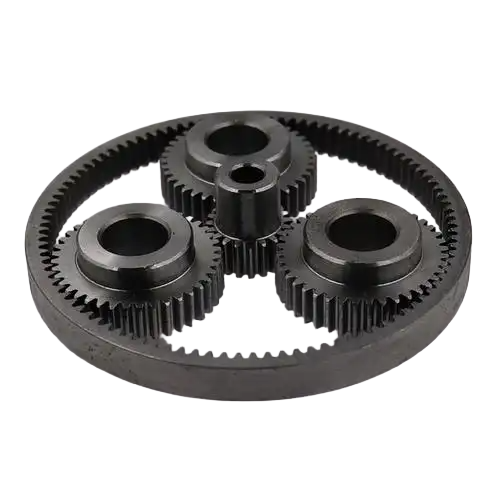

The planetary gear set provides multiple gear ratios for smooth transitions between forward and reverse gears.
- Funktion: Generates gear ratios by locking components (sun gear, planet gears, or ring gear) to control power flow.
- Components:
- Sun Gear: Central gear connected to the input shaft.
- Planet Gears: Multiple gears on a carrier, meshing with sun and ring gears.
- Ring Gear: Outer gear surrounding planet gears.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sun Gear Teeth | Number of teeth | 20–40 teeth | Gear hobbing or grinding |
| Ring Gear Teeth | Number of teeth | 60–100 teeth | Broaching or gear shaping |
| Gear Ratios | Forward and reverse ratios | 3.5:1 (1st gear) to 0.7:1 (overdrive) | N/A (design-dependent) |
| Material | Durability requirement | Hardened steel or alloy | Forging, heat treatment, and machining |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Sun and Planet Gears: Forged from high-strength steel, followed by gear hobbing or grinding to achieve precise tooth profiles. Heat treatment (e.g., carburizing) enhances durability.
- Ring Gear: Formed via broaching or gear shaping, with internal teeth cut to exact specifications. Heat treatment ensures wear resistance.
- Planet Carrier: Cast or forged from steel, with precision machining for gear mounting points to ensure alignment.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Gears undergo surface hardening and dimensional inspections to meet tight tolerances (e.g., ISO 6–8 gear quality standards).
- Operation: Gear ratios are achieved by locking components via clutches or bands, controlled hydraulically.
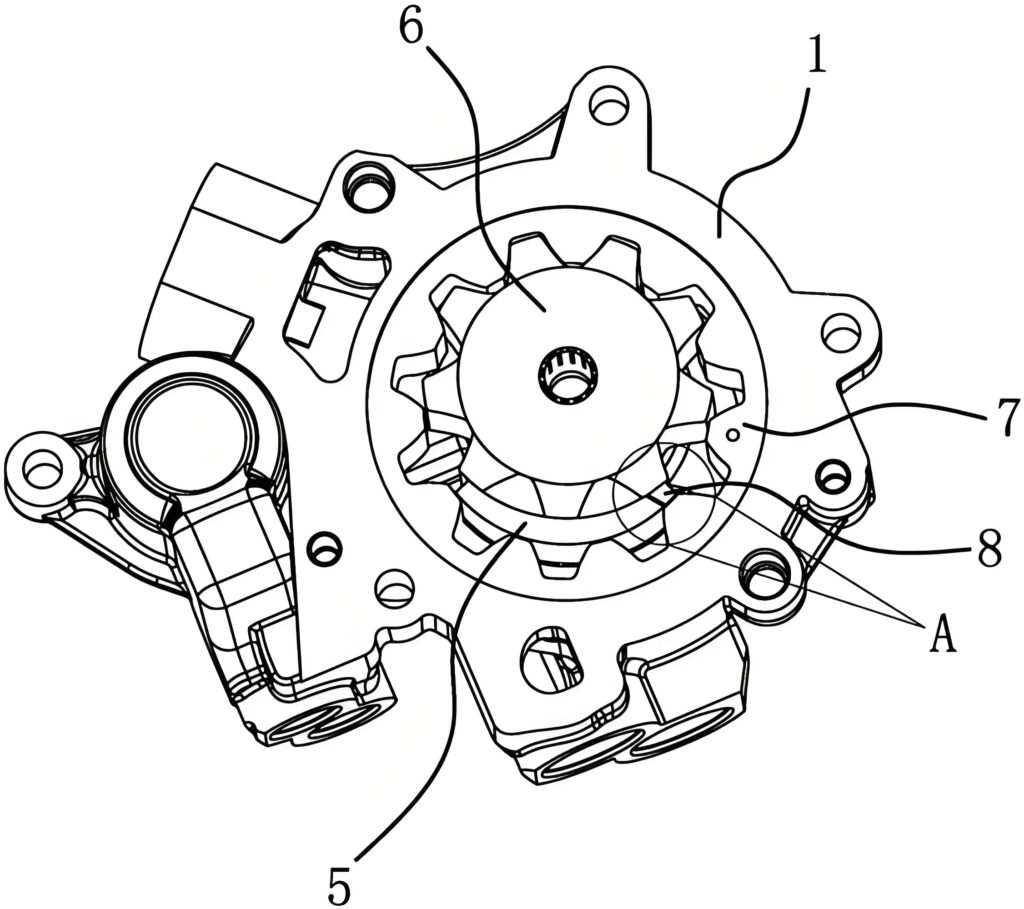
3. Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system uses pressurized transmission fluid to actuate clutches, bands, and other components.
- Funktion: Distributes automatic transmission fluid (ATF) to control gear engagement and lubrication.
- Components:
- Fluid Passages: Tubes and channels directing ATF.
- Seals and Gaskets: Prevent fluid leaks.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid Pressure | Operating pressure | 50–200 psi | N/A (functional parameter) |
| Fluid Type | ATF specification | Dexron VI, Mercon V, or OEM-specific | N/A (fluid not manufactured) |
| Seal Material | Durability and flexibility | Neoprene, silicone, or rubber | Injection molding or extrusion |
| Passage Material | Durability | Aluminum or steel | Casting or CNC machining |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Fluid Passages: Cast into the transmission case using aluminum or steel, with CNC machining to ensure precise channel dimensions for consistent fluid flow.
- Seals and Gaskets: Produced via injection molding or extrusion, using heat- and oil-resistant materials like neoprene or silicone. Precision cutting ensures proper fitment.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Passages are pressure-tested for leaks, and seals undergo durability testing to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Maintenance: Regular fluid checks and seal replacements prevent leaks and ensure consistent pressure.
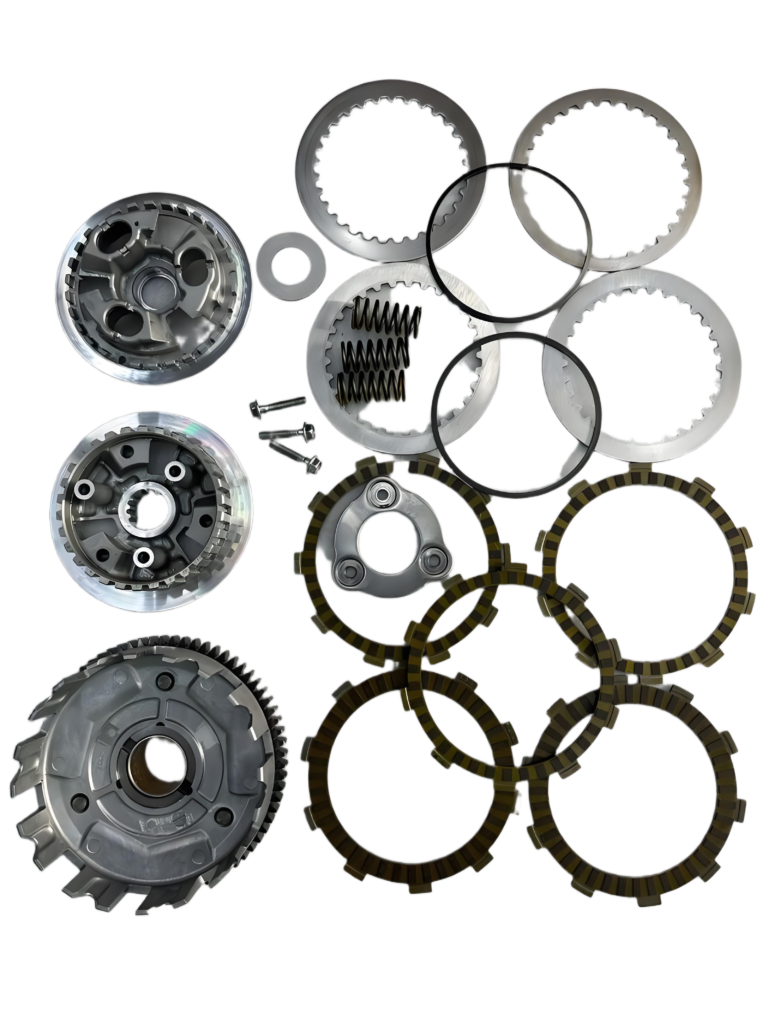

4. Clutch Packs
Clutch packs engage and disengage gears within the planetary gear set.
- Funktion: Use hydraulic pressure to compress friction and steel plates, locking gears for power transfer.
- Components:
- Friction Plates: Lined with friction material.
- Steel Plates: Provide a stable surface.
- Clutch Drum and Piston: House and actuate plates.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plate Count | Number per clutch pack | 4–8 plates | Stamping (steel), bonding (friction material) |
| Friction Material | Heat and wear resistance | Cellulose, Kevlar, or composite | Coating or bonding to steel core |
| Operating Pressure | Hydraulic pressure required | 100–300 psi | N/A (functional parameter) |
| Drum Material | Durability | Steel or aluminum | Casting or forging, CNC machining |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Friction Plates: Steel cores are stamped, then coated or bonded with friction materials (e.g., Kevlar) using adhesive or thermal bonding processes.
- Steel Plates: Stamped from high-strength steel, with surface grinding for flatness and heat treatment for durability.
- Clutch Drum and Piston: Cast or forged, followed by CNC-Bearbeitung for precise tolerances. Drums are balanced to prevent vibration.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Plates are tested for friction coefficient and wear resistance, ensuring consistent performance under high pressure.
- Operation: Hydraulic pressure compresses plates to engage gears, controlled by the valve body.
5. Bands
Bands are steel straps with friction material that hold or release planetary gear components.
- Funktion: Stop or slow drum rotation to control gear engagement.
- Typen:
- Forward Drive Band: Engages forward gears.
- Reverse Band: Engages reverse gear.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band Width | Forward vs. reverse | Forward: 40–60 mm; Reverse: 20–40 mm | Stamping and bonding |
| Friction Material | Durability | Asbestos-free composites | Adhesive bonding to steel strap |
| Actuation Pressure | Hydraulic pressure required | 50–150 psi | N/A (functional parameter) |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Steel Strap: Stamped from high-strength steel, with heat treatment to enhance tensile strength.
- Friction Lining: Bonded to the strap using high-temperature adhesives, with materials like Kevlar or composites for heat resistance.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Bands are tested for tensile strength and friction performance to ensure reliable engagement.
- Operation: Hydraulic pressure tightens the band around a drum to hold it stationary.

6. Oil Pump
The oil pump pressurizes transmission fluid to operate the hydraulic system and lubricate components.
- Funktion: Circulates ATF to clutches, bands, and other components.
- Type: Gear or vane pump, typically mounted between the torque converter and gear set.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pump Type | Design | Gear or vane pump | Casting, CNC machining |
| Flow Rate | Fluid delivery | 10–20 liters/min | N/A (functional parameter) |
| Operating Pressure | Pressure generated | 50–200 psi | N/A (functional parameter) |
| Material | Durability | Aluminum or steel | Casting, precision machining |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Pump Housing: Cast from aluminum or steel, with CNC machining for precise internal tolerances.
- Gears or Vanes: Forged or machined from hardened steel, with gear hobbing or grinding for accurate tooth profiles in gear pumps.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Pumps are tested for pressure output and fluid flow to ensure consistent performance.
- Maintenance: Pump failure can cause slipping or overheating, requiring regular fluid level checks.
7. Valve Body
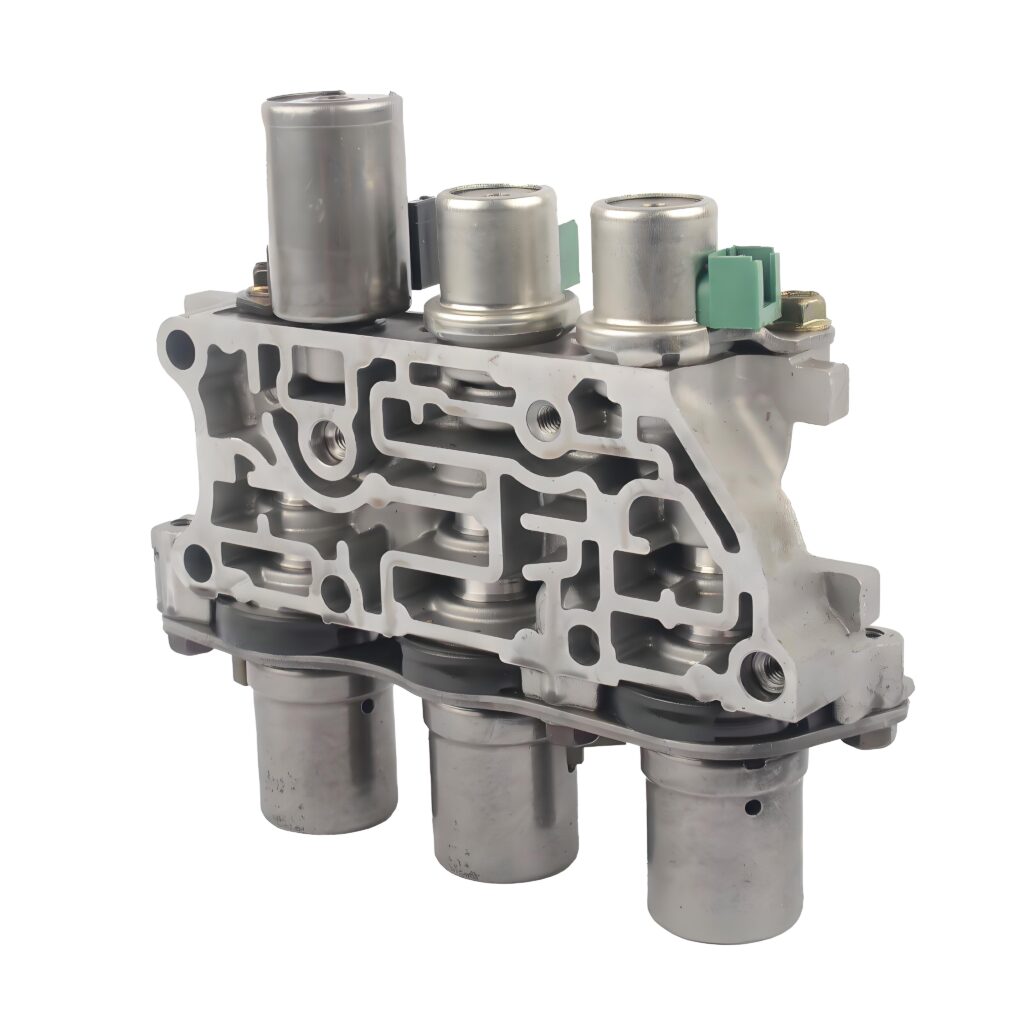

The valve body directs fluid to control gear shifts.
- Funktion: Regulates fluid flow to clutches and bands based on TCM signals.
- Components:
- Valves: Governor, throttle, shift, and pressure regulator valves.
- Solenoids: Electrically controlled actuators.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solenoid Count | Number per valve body | 4–10 solenoids | Assembly of machined and molded parts |
| Valve Material | Durability | Aluminum or steel | Casting, CNC machining |
| Operating Voltage | Solenoid actuation | 12–24 V | N/A (functional parameter) |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Valve Body Housing: Cast from aluminum, with CNC machining for precise fluid channels and valve seats.
- Valves and Solenoids: Valves are machined from steel or aluminum, while solenoids are assembled from copper windings and molded plastic housings.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Valve bodies are pressure-tested for leaks and electronically tested for solenoid functionality.
- Operation: TCM signals control solenoids to direct fluid, enabling precise shifts.
8. Transmission Control Module (TCM)

The TCM manages gear shifts and transmission performance electronically.
- Funktion: Processes sensor data to control solenoids and optimize shifting.
| Component | Spezifikation | Typical Range/Value | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor Type | Control unit type | Microcontroller or ECU-integrated | Surface-mount technology, PCB assembly |
| Sensor Inputs | Data sources | Throttle position, speed, load sensors | N/A (functional parameter) |
| Operating Voltage | Electrical requirement | 12 V (typical automotive system) | N/A (functional parameter) |
- Manufacturing Details:
- Circuit Board: Produced using surface-mount technology, with microcontrollers and resistors soldered onto printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- Housing: Injection-molded plastic or aluminum to protect electronics from heat and vibration.
- Qualitätskontrolle: TCMs undergo rigorous testing for signal processing and environmental durability (e.g., temperature cycling).
- Operation: Adjusts shift points using algorithms for efficiency and performance.
Maintenance and Common Issues
Proper maintenance extends transmission lifespan:
- Fluid Changes: Replace ATF every 30,000–60,000 miles with OEM-specified fluids (e.g., Dexron VI).
- Leak Inspections: Check seals and gaskets to prevent fluid loss.
- Diagnostic Checks: Monitor TCM performance with diagnostic tools.
Common issues include:
- Slipping Gears: Due to worn clutch packs or low fluid pressure.
- Overheating: Caused by contaminated fluid or inadequate cooling.
- Delayed Shifting: Linked to faulty solenoids or valve body issues.
Schlussfolgerung
The automatic transmission relies on components like the torque converter, planetary gear set, hydraulic system, clutch packs, bands, oil pump, valve body, and TCM, each manufactured with precision processes like casting, machining, and forging to ensure durability and performance. Understanding their functions, parameters, and manufacturing methods is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. Regular fluid changes, leak inspections, and professional repairs by certified technicians ensure reliable operation.
