Precision machining is critical in modern manufacturing, producing parts with high accuracy and tight tolerances. This guide explores CNC machining and CMM inspection, their roles, processes, and integration in achieving superior quality in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Introduction to CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process where pre-programmed software controls tools and machinery. It operates complex equipment such as mills, lathes, and routers to produce precise parts, achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.0001 inches (0.00254 mm).
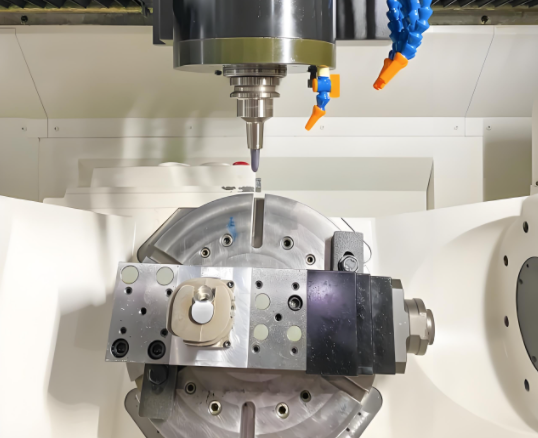

Types of CNC Machines
Different CNC machines serve specific purposes, as outlined below:
| Type | 설명 |
|---|---|
| CNC Milling Machine | Used for cutting and drilling, ideal for complex shapes. |
| CNC 선반 | Rotates the workpiece against a cutting tool, suitable for cylindrical parts. |
| CNC Router | Cuts materials like wood, plastic, and metal, often used for prototyping. |
| CNC Plasma Cutter | Uses a plasma torch to cut steel and other metals. |
| CNC Laser Cutter | Employs a laser for high-precision cutting or engraving. |
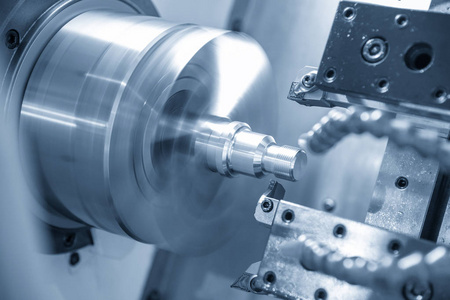




CNC 가공의 작동 원리
The process starts with a digital design created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, converted into G-code via Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. The G-code directs the CNC machine’s tool movements, including speed, feed rate, and positioning, ensuring automated and precise operation.
CNC 가공의 장점
- 정밀도: Achieves tolerances of ±0.0001 inches (0.00254 mm).
- 반복성: Consistently produces identical parts.
- 효율성: Automation reduces production time and errors.
- 유연성: Easily reprogrammed for different parts.
Introduction to CMM Inspection
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspection uses a coordinate measuring machine to assess a part’s geometric characteristics. A probe detects surface points to measure dimensions and shapes, with modern CMMs achieving accuracies of 0.5 microns.
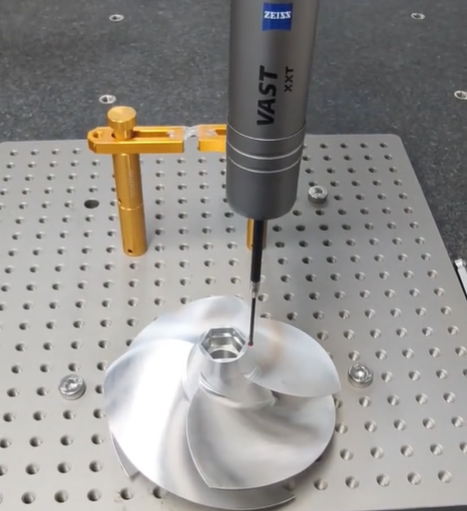

Types of CMMs
CMMs vary by design and application, as shown below:
| Type | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Bridge CMM | Most common, with a bridge structure moving along X, Y, Z axes. |
| Gantry CMM | Larger, used for measuring large parts like vehicle bodies. |
| Horizontal Arm CMM | Suitable for long, narrow parts or assemblies. |
| Portable CMM | Handheld, ideal for on-site measurements. |
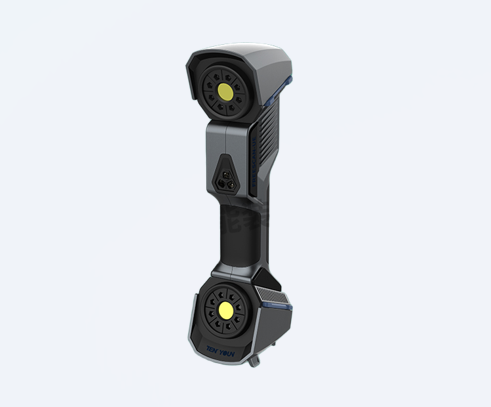
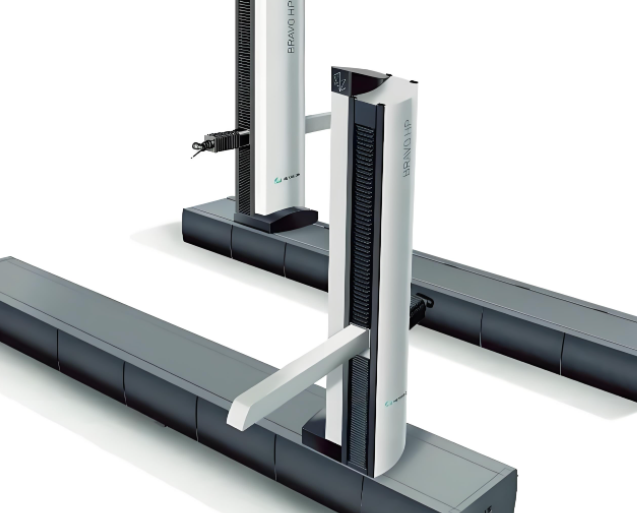



How CMM Inspection Works
A CMM moves a probe along X, Y, Z axes to contact or scan a part’s surface, recording point coordinates. These data are compared to the original CAD model to identify deviations, ensuring compliance with design specifications.
Role of CMM in Quality Control
CMM inspection verifies that parts meet stringent dimensional and tolerance requirements, critical in industries like aerospace and medical devices. It supports quality assurance by providing reliable measurement data.
Integration of CNC Machining and CMM Inspection
CMM inspection ensures CNC-machined parts meet design specifications, particularly for critical features like holes, slots, and surfaces. It is vital in industries requiring high precision, reducing rework and scrap.
Quality Control Process in CNC Machining
Quality control involves multiple stages to ensure parts meet standards:
- Raw Material Inspection: Verifies material quality before machining.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Evaluates the first produced part.
- In-Process Inspection: Monitors dimensions during machining.
- Assembly and Fit Inspection: Ensures parts align correctly in assemblies.
- Final Inspection: Confirms finished parts meet all specifications.
Tools and Techniques for Inspection
Beyond CMMs, inspection tools include calipers, micrometers, optical comparators, and surface roughness testers. CMM software like PC-DMIS and Metrolog X4 enhances measurement and data analysis capabilities.
Benefits of Integrating CMM with CNC Machining
- Enhanced Accuracy: Ensures parts meet tight tolerances.
- Reduced Inspection Time: Automated measurements are faster than manual methods.
- Increased Productivity: Minimizes rework and scrap.
- Improved Quality Assurance: Provides detailed documentation and traceability.

결론
CNC machining and CMM inspection are integral to 정밀 제조, delivering high-quality parts with tight tolerances. Their integration enhances accuracy, efficiency, and reliability, meeting the demands of industries like aerospace and medical devices. As technology advances, these processes will continue to evolve, driving innovation in manufacturing.
