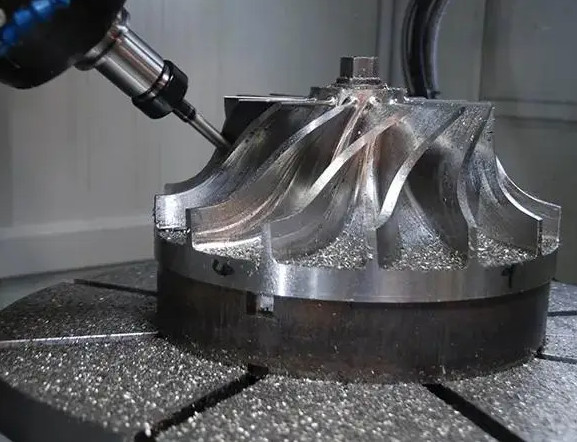
CNC milling, or Computer Numerical Control milling, is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of precise and complex parts across various industries. This guide provides a detailed exploration of CNC milling, including its historical development, key advantages, and practical applications. By focusing on technical details and practical insights, this article aims to offer a clear, professional, and systematic understanding of CNC milling for engineers, manufacturers, and enthusiasts.
History of CNC Milling in China
The introduction of CNC milling in China began in the late 1970s as part of the country’s economic reforms. During this period, China imported CNC machine tools from countries like Japan, Germany, and the United States, primarily for strategic sectors such as aerospace and defense. Limited by high costs and a lack of expertise, early adoption was slow, but research institutes and state-owned enterprises, such as those in Beijing and Shenyang, started reverse-engineering imported systems. By the 1980s, domestic manufacturers like Shenyang Machine Tool Group began producing basic CNC milling machines, marking the initial steps toward technological self-reliance.
The 1990s and 2000s saw significant growth in China’s CNC milling industry, fueled by economic liberalization and foreign investment. Government initiatives, such as the 863 Program, supported the development of advanced manufacturing technologies, while joint ventures with companies like Siemens and Fanuc facilitated technology transfer. By the late 1990s, firms like Huazhong CNC and GSK CNC Equipment Co. produced competitive machines, and China’s entry into the WTO in 2001 boosted demand for precision components in industries like automotive and electronics. By the end of the 2000s, China had become the world’s largest consumer and producer of CNC machine tools.
Since the 2010s, China has solidified its position as a global leader in CNC milling, driven by the “Made in China 2025” initiative, which emphasized intelligent manufacturing. Domestic manufacturers now produce advanced CNC milling machines, including five-axis systems, competing with global brands. Companies like DMG Mori China and Mazak China have expanded market share, while affordable CNC machines have empowered small and medium-sized enterprises in regions like Guangdong. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, has further enhanced China’s CNC milling capabilities, making it a cornerstone of the nation’s manufacturing prowess.

Advantages of CNC Milling
CNC milling offers numerous advantages over traditional manual milling and other manufacturing methods. These benefits stem from its automation, precision, and versatility, making it a preferred choice for producing high-quality parts.
Precision and Accuracy: CNC milling machines achieve tolerances ranging from 0.01 mm to 0.03 mm, with repeatability as low as 0.003 mm to 0.01 mm. This precision is critical for industries like aerospace and medical, where parts must meet exact specifications. The use of computer-controlled movements eliminates human error, ensuring consistent results that closely match CAD models.
반복성: Once a program is set, CNC mills can produce identical parts repeatedly with minimal variation. This is essential for batch production, where uniformity is required across thousands of components. For example, in automotive manufacturing, CNC milling ensures that engine blocks and gears meet consistent standards.
다용도성: CNC milling is compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals (aluminum, steel, titanium, brass), plastics, composites, and wood. Multi-axis machines (3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis) enable the production of complex geometries, such as curved surfaces, slots, and intricate contours, which are difficult or impossible with manual methods.
Efficiency and Productivity: CNC mills operate autonomously after programming, reducing the need for constant operator supervision. They can run 24/7 without breaks, significantly increasing production speed compared to manual machining. For instance, a CNC mill can complete a part in minutes, whereas manual milling might take hours.
Reduced Material Waste: 그리고 precision of CNC milling minimizes faulty cuts, reducing material waste. This is particularly valuable when working with expensive materials like titanium or high-strength alloys, lowering overall production costs.
Safety: CNC machines are typically enclosed, reducing the risk of operator injury compared to manual machining. Automation eliminates many hazards associated with handling tools, enhancing shop floor safety.
Cost-Effectiveness: Despite high initial costs, CNC milling reduces labor expenses by requiring fewer operators. The ability to produce parts quickly and accurately also lowers per-unit costs, especially in large-scale production.
The following table summarizes the key advantages of CNC milling:
| Advantage | 설명 | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 정밀도 | Tolerances of 0.01–0.03 mm, repeatability of 0.003–0.01 mm | Ensures parts meet exact specifications |
| 반복성 | Consistent production of identical parts | Ideal for batch production |
| 다용도성 | Works with metals, plastics, composites, and wood | Suitable for diverse applications |
| 효율성 | Autonomous operation, 24/7 production | Increases output, reduces labor costs |
| Safety | Enclosed systems reduce operator risks | Enhances workplace safety |
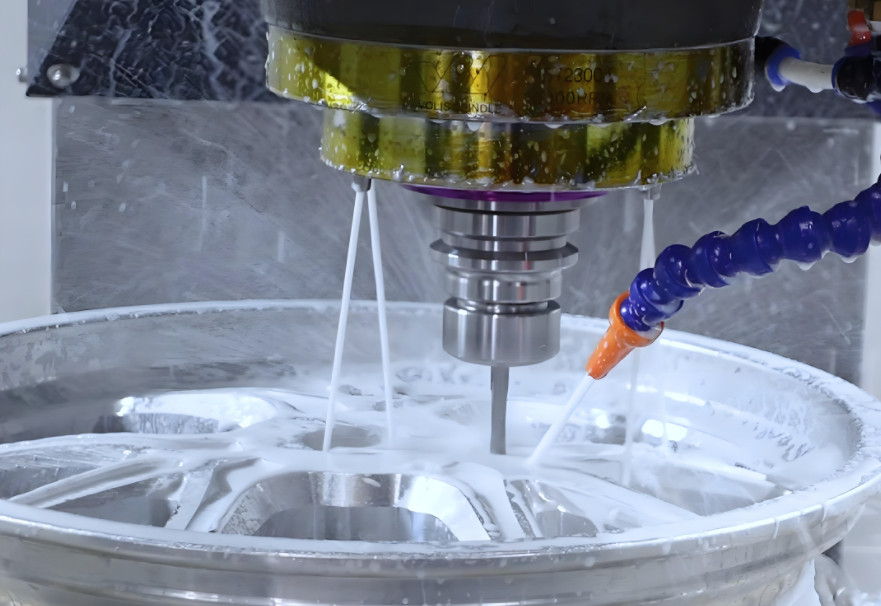

CNC 밀링의 응용 분야
CNC milling is widely used across industries due to its ability to produce precise, complex, and reliable parts. Its applications span prototyping, batch production, and the creation of custom components for specialized purposes.
Aerospace Industry: CNC milling is critical for manufacturing components like engine parts, structural elements, and instrument panels. These parts often require tight tolerances (e.g., 0.001 inches) and complex geometries, such as turbine blades or manifolds. Materials like titanium and high-strength alloys are commonly used due to their durability and lightweight properties.
Automotive Industry: CNC milling produces engine blocks, gears, transmission components, and prototypes. The high speed and repeatability of CNC mills make them ideal for mass production, where thousands of identical parts are needed. For example, aluminum engine blocks are machined to precise dimensions to ensure optimal performance.
Medical Industry: CNC milling is used to create surgical instruments, prosthetics, and orthotics. The ability to produce custom parts, such as a tailored hip replacement, is invaluable. CNC mills also fabricate FDA-approved medical devices with high precision, ensuring safety and functionality.
Electronics Industry: CNC milling is employed to manufacture heat sinks, amplifier housings, and other components. For instance, the aluminum chassis of devices like the Apple MacBook is produced using CNC milling, achieving a smooth finish and precise dimensions.
Prototyping and Custom Parts: CNC milling excels in rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to create one-off parts for testing or small-scale production. It supports iterative design processes by enabling quick modifications to CAD models, which are then translated into machined parts.
Tool and Die Making: CNC milling is used to create molds and dies for injection molding and other manufacturing processes. High-precision copper mold patterns are often produced using 5-axis CNC mills to achieve complex contours.
Other Applications: CNC milling is also used in industries like defense, energy, and consumer goods. For example, it produces components for firearms, wind turbine parts, and household appliances, showcasing its versatility across different scales and requirements.
The following table highlights key applications of CNC milling across industries:
| 산업 | 애플리케이션 | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 항공우주 | Engine components, structural parts | Turbine blades, impellers, manifolds |
| 자동차 | Engine blocks, gears, prototypes | Transmission components |
| 의료 | Surgical instruments, prosthetics | Custom hip replacements |
| 전자 제품 | Heat sinks, housings | Aluminum MacBook chassis |
| 프로토타이핑 | One-off parts, iterative designs | Custom robotic components |






Limitations of CNC Milling
While CNC milling offers significant advantages, it also has limitations that manufacturers must consider when selecting it for specific projects.
높은 초기 비용: CNC milling machines are expensive, with basic models costing around $2,000 and high-end multi-axis machines reaching $100,000 or more. Maintenance and repair costs can also be substantial, posing a barrier for small businesses or startups.
Skilled Labor Requirements: Operating CNC mills requires trained personnel to program and maintain the machines. While automation reduces the need for constant supervision, initial setup and programming demand expertise in CAD/CAM software and G-code.
Design Constraints: Some complex geometries, such as hidden features or intricate internal structures, may be difficult or impossible to machine, even with multi-axis mills. Manufacturers must design parts with machining capabilities in mind.
재료 제한: While versatile, CNC milling may not be suitable for all materials. For example, certain ceramics or brittle materials may require specialized tools or alternative processes to avoid cracking.
Despite these limitations, CNC milling remains a highly effective manufacturing method when applied appropriately, with careful consideration of project requirements and machine capabilities.
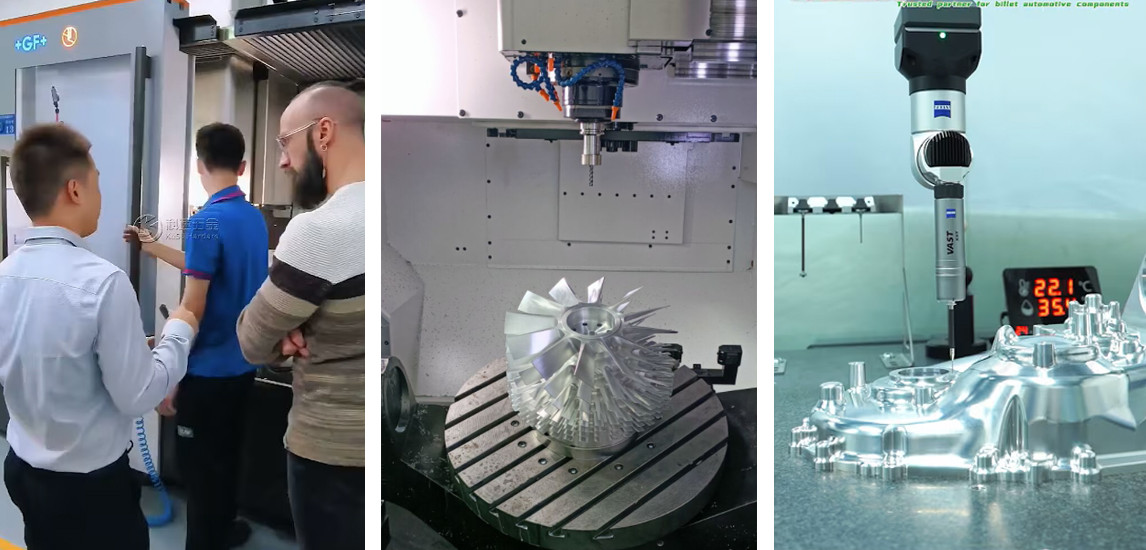
KeSu's CNC Milling Solutions for Your Needs
Processing complex-shaped precision part products places specific demands on the machining capability: first, it must support five-axis machining; second, it must ensure high CNC milling machining precision; third, it must have strong chip removal capabilities for batch processing; and finally, it must offer high space utilization. KeSu’s five-axis high-speed CNC machining center not only achieves micron-level machining precision but also meets your equipment needs for processing complex-shaped precision products.
결론
CNC milling is a transformative manufacturing process that combines precision, efficiency, and versatility to produce high-quality parts for a wide range of industries. Its history, from the punched tape systems of the 1940s to today’s advanced multi-axis machines, demonstrates a commitment to improving manufacturing capabilities. The advantages of precision, repeatability, and automation make CNC milling indispensable in aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics applications, among others. While limitations such as high costs and skilled labor requirements exist, the benefits often outweigh these challenges for large-scale or precision-driven projects. By understanding the technical aspects and practical applications of CNC milling, manufacturers can leverage this technology to achieve reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality production outcomes.
