Metal 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a cutting-edge technology that transforms digital designs into precise metal components. This article provides a concise, professional overview of the key advantages of metal 3D printing and its diverse applications across industries.

Advantages of Metal 3D Printing
1. Streamlined Production Efficiency
Metal 3D printing enables rapid production of complex metal parts in a single step, eliminating multiple stages required in traditional manufacturing. This reduces lead times and simplifies workflows. Digital design integration minimizes manual processes, enhancing production speed and scalability.
2. Cost Reduction
By using only the necessary material, metal 3D printing minimizes waste compared to subtractive methods, lowering material costs. Automated processes reduce labor expenses, and the elimination of specialized tooling further optimizes costs for both small-batch and large-scale production.

3. Precision and Quality Control
The technology produces highly accurate, intricate parts with consistent quality. Advanced control over layer-by-layer construction reduces defects and ensures tight tolerances, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and reliability.
4. Tailored Customization
Metal 3D printing supports on-demand customization without the need for costly molds or retooling. This flexibility allows manufacturers to meet specific client needs efficiently, enabling bespoke solutions across various sectors.

5. Environmental Efficiency
Additive manufacturing promotes sustainability by reducing material waste and energy consumption. Localized production capabilities decrease transportation needs, contributing to a lower carbon footprint and aligning with eco-conscious manufacturing goals.
Industry Applications of Metal 3D Printing
1. Industrial Manufacturing
Metal 3D printing is extensively used to produce automotive components, machinery parts, and complex assemblies like gears and brackets. Its ability to create lightweight, durable parts enhances performance and reduces production timelines.

2. Healthcare
In the medical field, the technology enables the creation of patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and dental devices. Its precision and customization capabilities improve patient outcomes and streamline production compared to conventional methods.

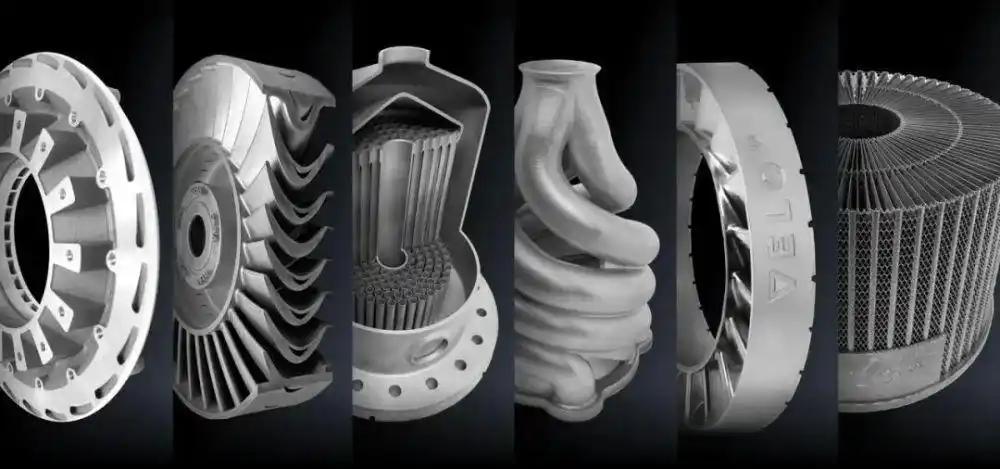
3. Aerospace
Aerospace applications include the production of lightweight, high-strength components such as turbine blades and fuel injectors. Metal 3D printing meets rigorous industry standards, improving fuel efficiency and part performance.
4. Construction
The construction sector utilizes metal 3D printing for structural elements and custom fittings. The technology supports rapid production of tailored designs, reducing costs and lead times for architectural projects.

Conclusion
Metal 3D printing delivers significant advantages, including enhanced efficiency, cost savings, precision, customization, and sustainability. Its applications across manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and construction demonstrate its transformative potential. As adoption grows, this technology will continue to drive innovation, offering scalable, high-quality solutions for diverse industry needs.
