Manufacturing engine components involves several critical aspects, ranging from material selection to processing methods, environmental factors, and quality control. The following are key considerations for producing high-quality engine parts.
Material Selection
Material selection plays a crucial role in determining the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of engine components. To meet the high demands of modern engines, the chosen material must possess various essential properties:
| Property | Description | Materials Used |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Properties | High strength, rigidity, and fatigue resistance for high-stress environments. | Titanium Alloys, Steel Alloys |
| High-Temperature Performance | Materials must maintain strength and performance at elevated temperatures. | Nickel-based Alloys, High-Temperature Steel |
| Corrosion Resistance | Ability to resist degradation from chemicals, fuels, and cooling fluids. | Aluminum Alloys, Titanium Alloys |
| Machinability | The ease with which the material can be processed and shaped without excessive wear on tools. | Aluminum Alloys, Cast Iron |
| Cost | Balancing material performance with cost-effectiveness. | Steel, Aluminum |
Processing Methods
The manufacturing of engine components requires precise processing methods to ensure accuracy, stability, and efficiency. Some of the key methods include:
| Processing Method | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Machining | Traditional methods such as milling, turning, and drilling to achieve precise shapes and dimensions. | Most Engine Parts |
| Precision Machining | Fine machining processes like EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) for extremely tight tolerances. | High-Precision Components |
| Chemical Machining | Using chemical processes to etch and shape materials, especially for intricate or thin components. | Complex or Micro Components |
| Laser Machining | Using lasers for high-precision cutting or engraving, especially for hard materials. | Hard-to-machine Materials |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing to create complex shapes and reduce material waste, ideal for small batches. | Customized and Lightweight Components |
| Heat Treatment | Processes like quenching and tempering to alter the hardness, toughness, and fatigue resistance of the material. | Metal Parts with High Wear Resistance |
Production Environment
Maintaining an optimal production environment is crucial to ensure the high quality of engine parts. Key factors include:
- Equipment Calibration: Regular maintenance and calibration of machinery to maintain precision.
- Cleanliness: The workshop should be free from dust, dirt, and oil contamination.
- Temperature & Humidity Control: Variations can affect material properties and machining accuracy.
- Cleanroom Technology: For high-end components, maintaining a cleanroom environment is essential to avoid contamination.
Safety Considerations
Ensuring safety throughout the manufacturing process is critical to avoid accidents and maintain operational efficiency:
- Automation: Implementing automation to reduce human error and enhance precision.
- Protective Measures: Adequate safety guards, personal protective equipment (PPE), and safety protocols.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Operators must be trained on safe and effective use of equipment.
- Emergency Response: Having emergency protocols in place to handle accidents quickly and efficiently.
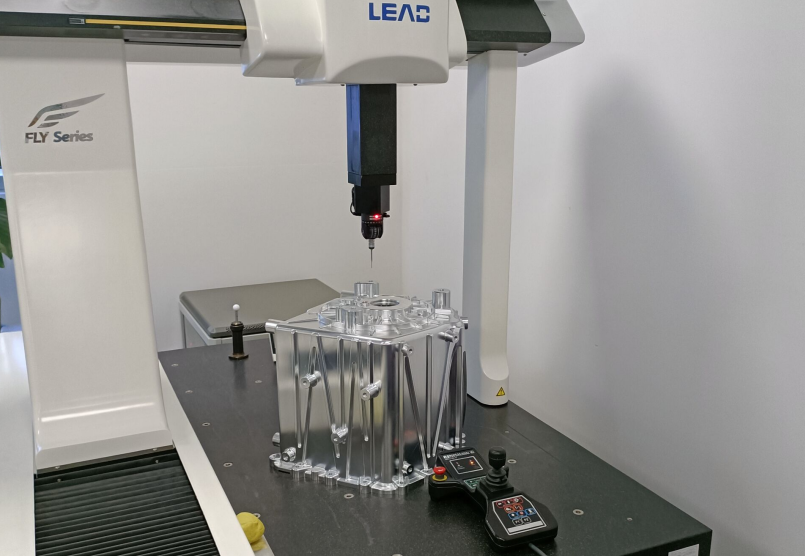
Quality Control
Quality control is essential to ensure that all components meet the stringent performance and durability standards required for engine applications:
| Quality Control Aspect | Description | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inspection | Measuring the size, shape, and alignment of the component to ensure it meets the design specifications. | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) |
| Material Testing | Testing the material properties such as hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance. | Hardness Testers, Tensile Test Machines |
| Non-Destructive Testing | Testing for internal flaws or defects without damaging the part, such as through X-ray or ultrasonic testing. | Ultrasonic, X-Ray, Dye Penetrant Testing |
| Process Control | Using statistical methods to monitor and control the manufacturing process. | SPC (Statistical Process Control) |
| Traceability | Maintaining a record of each component’s production history for accountability. | ERP Systems, Production Logs |
| Durability Testing | Conducting long-term tests to simulate real-world operational conditions and ensure reliability. | Fatigue Testing, Thermal Cycling |

Conclusion
The manufacturing of engine components requires precise planning and execution. By addressing critical factors such as material selection, processing methods, environmental conditions, safety, and quality control, manufacturers can ensure the production of high-quality, reliable parts. Every stage, from material selection to final testing, must be optimized to guarantee performance, durability, and efficiency in the final product.