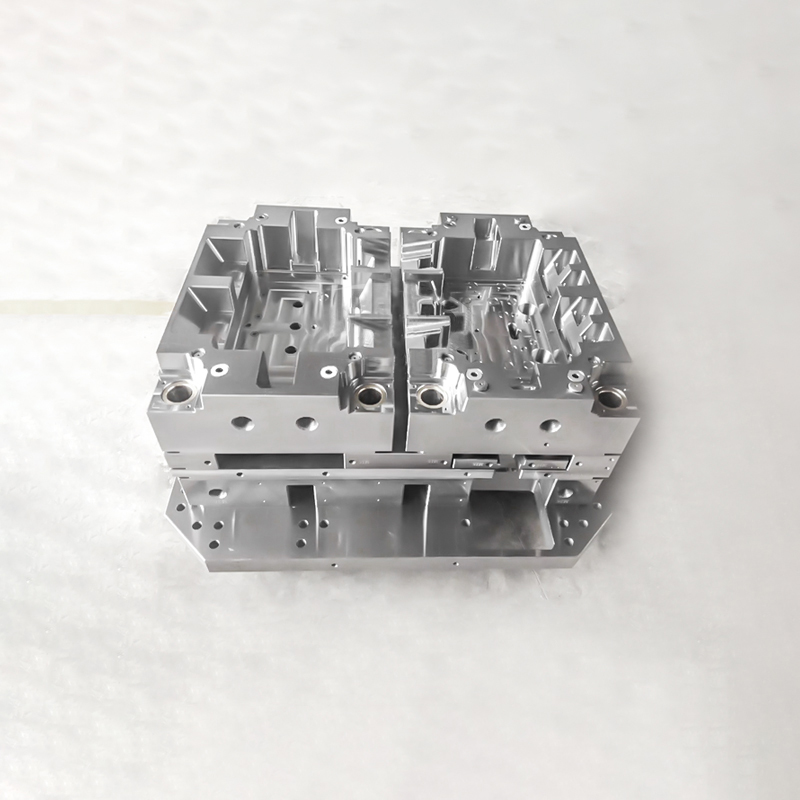
Rapid tooling has transformed modern manufacturing by enabling the swift production of molds for low-volume and medium-volume manufacturing, significantly reducing costs and lead times compared to traditional methods. In China, a global manufacturing hub, rapid tooling services leverage advanced technologies and materials like aluminum 7075 and soft steel P20 to deliver high-quality molds for injection molding and other processes. These services cater to industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, and aerospace, offering flexibility and precision for product development and market entry. This guide explores the intricacies of rapid tooling in China, focusing on mold-making techniques, injection molding, and their applications. Detailed parameters, industry insights, and technical considerations provide a comprehensive understanding of these processes, highlighting their role in streamlining manufacturing workflows.
Fundamentals of Rapid Tooling
Rapid tooling refers to the expedited production of molds and tooling, typically for injection molding or die casting, to support low-volume to medium-volume manufacturing. Unlike traditional tooling, which uses hardened steel and requires months of lead time, rapid tooling employs softer, easier-to-machine materials and streamlined processes to create molds machining in days. In China, rapid tooling is optimized for cost efficiency, with lead times as short as 5–7 days and cost savings of 30–40% compared to conventional methods. The process is ideal for bridging the gap between prototyping and full-scale production, enabling businesses to test markets, validate designs, and produce functional parts quickly.
Materials for Rapid Tooling
Rapid tooling relies on materials that balance machinability, durability, and cost. Common choices include:
- Aluminum 7075: With a tensile strength of 570 MPa and excellent thermal conductivity, aluminum 7075 is ideal for molds with lifespans of up to 5,000–10,000 cycles. Its machinability reduces lead times to 5–7 days.
- Soft Steel P20: Offering a yield strength of 800 MPa, P20 is suitable for molds with lifespans of 50,000–100,000 cycles. It supports medium-volume production with lead times of 7–10 days.
- Pre-Hardened Tool Steels: Used for high-volume rapid production tooling, these steels achieve lifespans exceeding 1,000,000 cycles, with lead times of 10–14 days.
Master Unit Die (MUD) Systems
A key innovation in rapid tooling is the use of Master Unit Die (MUD) systems, where reusable mold bases accommodate custom core and cavity inserts. This approach reduces machining time by focusing only on part-specific components, achieving cost savings of 30–40%. MUD systems are versatile, supporting aluminum and P20 inserts, and are widely used for injection molding in automotive and electronics industries.
Tooling Design Considerations
Effective rapid tooling requires careful design to ensure mold longevity and part quality. Key considerations include:
- Draft Angles: Angles of 1–3 degrees facilitate part ejection, reducing wear on molds making.
- Uniform Wall Thickness: Thicknesses of 1.5–3 mm minimize defects like sink marks and ensure consistent molding.
- Gate Placement: Strategic gate locations optimize material flow, reducing cycle times by 10–20%.
- Cooling Channels: Conformal cooling channels improve heat dissipation, shortening cycle times by up to 30%.

Rapid Injection Molding: Precision and Efficiency
Rapid injection molding uses rapid tooling to produce high-quality plastic parts with production-grade materials, offering tolerances of ±0.05 mm and surface finishes as fine as Ra 1.6 μm. This process is ideal for low-volume runs of 500–10,000 parts, with lead times of 7–12 days. In China, rapid injection molding supports industries requiring functional parts with precise mechanical properties, such as automotive dashboards and medical device housings.
Material Options
Rapid injection molding supports a wide range of thermoplastics and thermosets, including:
- ABS: Tensile strength of 40–50 MPa, used for consumer electronics and automotive parts.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Impact strength of 60–70 MPa, ideal for medical devices and optical components.
- Nylon (PA6/PA66): Tensile strength of 50–80 MPa, used for wear-resistant components like gears.
- PEEK: High-temperature resistance up to 250°C and tensile strength of 95 MPa, used in aerospace and medical applications.
Surface Finish Optimization
Surface finish significantly impacts tooling cost and lead time. Standard finishes like SPI C-1 (machined) or D-2 (bead blasted) are cost-effective, requiring minimal mold machining preparation. High-polish finishes like SPI A-1 demand extensive polishing, increasing lead times by 2–3 days and costs by 10–20%. Specifying only necessary finish levels optimizes efficiency, particularly for non-cosmetic surfaces.
Process Capabilities
Rapid injection molding supports advanced techniques like insert molding and overmolding. Insert molding integrates metal or plastic inserts into parts, achieving tolerances of ±0.1 mm. Overmolding combines multiple materials, such as TPE over PC, for enhanced grip or aesthetics. Injection presses with clamping forces of 50–500 tons accommodate various part sizes, from small medical components to large automotive panels.
Tooling Strategies for Different Production Needs
Rapid tooling encompasses multiple strategies tailored to production volume and part requirements. These strategies ensure cost-effective solutions for prototyping, market testing, and full-scale production.
Prototype Tooling
Prototype tooling produces molds for small-batch production, with lifespans of up to 5,000 cycles. Typically made from aluminum 7075, these molds are completed in 5–7 days and are ideal for validating moldability and material properties in automotive and consumer electronics applications. They offer cost savings of 30–40% compared to traditional molds making.
Bridge Tooling
Bridge tooling supports medium-volume production, with mold lifespans of up to 100,000 cycles. Using soft steel P20 or hybrid aluminum-steel combinations, these molds balance durability and cost, with lead times of 7–10 days. Bridge tooling is suited for market testing and pre-production runs in medical devices and robotics.
Rapid Production Tooling
Rapid production tooling creates molds for high-volume manufacturing, with lifespans exceeding 1,000,000 cycles. Made from hardened tool steels like H13 or S136, these molds incorporate features like hot runner systems and multi-cavity designs to maximize output. Lead times range from 10–14 days, making them suitable for large-scale automotive and industrial production.
Applications of Rapid Tooling in Industry
Rapid tooling serves a wide range of industries, leveraging China’s manufacturing capabilities to deliver high-quality parts with short lead times.
Automotive
The automotive industry uses rapid injection molding for components like dashboards, bumpers, and interior panels, with mold lives up to 100,000 cycles. Rapid tooling enables quick iterations during development, reducing time-to-market for new vehicle models. Materials like ABS and PC ensure durability and aesthetic quality.
Medical
Medical device manufacturing relies on rapid tooling for producing housings, connectors, and disposable components. Biocompatible materials like PEEK and PC are molded with tolerances of ±0.05 mm and surface finishes of Ra 1.6 μm. Rapid tooling supports small-batch production for clinical trials and market validation.
Electronics
Electronics manufacturing uses rapid tooling for plastic enclosures and connectors, achieving tolerances of ±0.05 mm. Rapid injection molding produces parts with high-precision features, such as snap-fits and mounting points, using materials like nylon and PC for durability and flame resistance.
Complementary Prototyping for Tooling Validation
While rapid tooling is the primary focus, complementary prototyping processes like CNC machining and vacuum casting play a critical role in validating mold designs and producing master patterns for tooling. These methods ensure that molds meet design specifications before production begins.
CNC Machining for Mold Components
CNC machining produces mold inserts and master patterns with tolerances of ±0.005 mm. Materials like aluminum 7075 and P20 steel are machined using 5-axis systems, ensuring precise cavity and core geometries. Lead times for mold components are typically 3–7 days, supporting rapid tooling timelines.
Vacuum Casting for Pre-Production Parts
Vacuum casting creates small batches of parts using silicone molds, with a mold life of 20–50 cycles. This process validates material properties and part designs before committing to injection molding, achieving tolerances of ±0.15 mm and lead times of 7–14 days. It is particularly useful for medical and consumer electronics applications.
Advantages of Rapid Tooling
Rapid tooling offers several benefits, particularly in China’s cost-competitive manufacturing environment.
Cost Efficiency
Rapid tooling reduces costs by 30–40% compared to traditional molds, using materials like aluminum and MUD systems to minimize machining time. Optimized mold making designs and minimal surface preparation further lower expenses.
Speed
Lead times for rapid tooling range from 5–7 days for prototype tooling to 10–14 days for production tooling. This speed accelerates product development and market entry, critical for industries like automotive and electronics.
Flexibility
Rapid tooling supports a range of production volumes and materials, enabling customization for specific applications. Design changes are easier to implement, with mold modifications completed in 2–5 days, compared to weeks for traditional tooling.

Challenges and Solutions in Rapid Tooling
Rapid tooling faces challenges that require specialized solutions to ensure quality and efficiency.
Mold Durability
Rapid tooling molds, particularly those made from aluminum, have shorter lifespans than hardened steel molds. Using hybrid materials, like P20 steel inserts in aluminum bases, extends mold life to 50,000–100,000 cycles. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and polishing, further enhances durability.
Material Compatibility
Some abrasive or high-temperature materials, like glass-filled nylon, accelerate mold wear. Selecting appropriate mold materials, such as P20 or pre-hardened steels, and applying surface treatments like nitriding improve compatibility and extend mold life by 20–30%.
Thermal Management
High molding temperatures can degrade softer mold materials. Conformal cooling channels and high-thermal-conductivity materials like aluminum 7075 dissipate heat efficiently, reducing cycle times by 30% and protecting mold integrity.
Rapid tooling in China provides a robust solution for low-volume and medium-volume manufacturing, leveraging advanced mold-making techniques and materials to deliver high-quality parts with short lead times. By focusing on injection molding and tailored tooling strategies, these services meet the demands of industries requiring precision, cost efficiency, and flexibility. From automotive components to medical devices, rapid tooling continues to drive innovation and efficiency in global manufacturing, supporting businesses in achieving faster market entry and optimized product development.
Rapid Tooling Manufacturing by Kesu Group
- Advanced equipment
Precision production and testing equipment with high stability. - Rich experience
More than 10 years experience in rapid mold manufacturing and injection molding, with independent design and development capability. - High quality, competitive price and fast delivery
With factory under systematic management, professional team and flexible production time to ensure satisfactory service. - One-stop service
As one of the best rapid mold companies, we support mold design and manufacturing, injection production, machining, assembly, packaging, delivery and other services. We can provide our customers with strong engineering support; this greatly reduces any potential quality risks that limit rapid time-to-market.
FAQ: Rapid Tooling Services
What is rapid tooling, and how does it differ from traditional tooling?
Rapid tooling creates molds for low-volume to medium-volume production using materials like aluminum 7075 or soft steel P20, with lead times of 5–14 days and cost savings of 30–40%. Traditional tooling uses hardened steel for high-volume production, requiring months of lead time and higher costs.
What materials are used in rapid injection molding?
Rapid injection molding supports thermoplastics like ABS (40–50 MPa tensile strength), polycarbonate (60–70 MPa), nylon (50–80 MPa), and PEEK (95 MPa), as well as thermosets, meeting requirements for automotive, medical, and electronics applications.
How long does it take to produce a rapid tooling mold?
Lead times vary by tooling type: prototype tooling takes 5–7 days, bridge tooling 7–10 days, and rapid production tooling 10–14 days, depending on complexity and material.
What industries benefit from rapid tooling?
Automotive, medical, electronics, and aerospace industries benefit from rapid tooling’s precision, speed, and flexibility, enabling efficient production of functional parts and market testing.